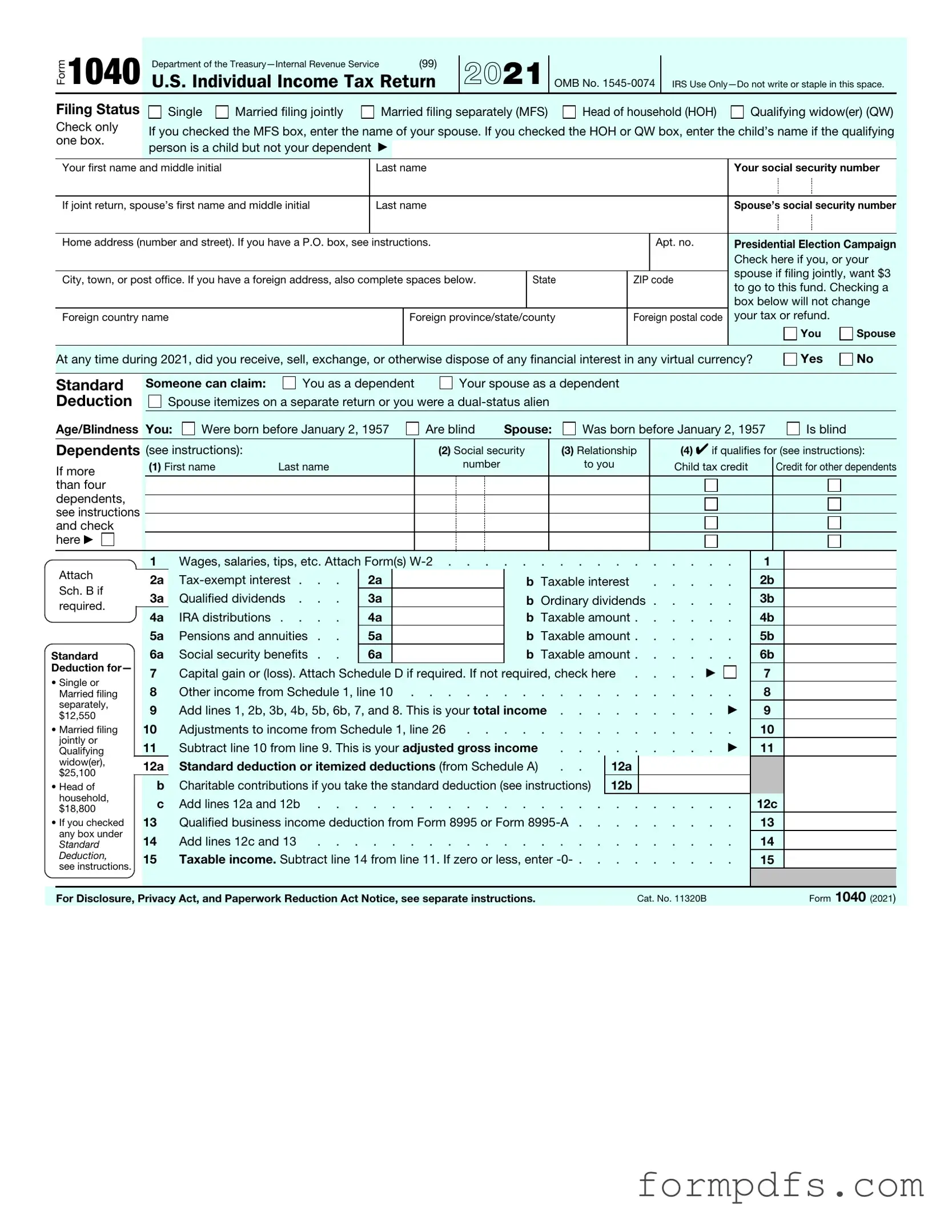
Blank IRS 1040 PDF Form
The IRS 1040 form is a critical document for individual taxpayers in the United States, serving as the primary means for reporting income, calculating taxes owed, and determining eligibility for various tax credits and deductions. This form encompasses a wide range of financial information, including wages, interest, dividends, and capital gains, allowing taxpayers to present a comprehensive picture of their annual earnings. Additionally, the 1040 form includes sections for claiming deductions, such as the standard deduction or itemized deductions, which can significantly reduce taxable income. Taxpayers may also need to report other income sources, such as self-employment earnings or rental income, depending on their financial situation. Furthermore, the form provides opportunities to claim tax credits, which can directly reduce the amount of tax owed. Understanding the intricacies of the 1040 form is essential for ensuring compliance with tax regulations and maximizing potential refunds. As the tax season approaches, familiarity with this form can help individuals navigate the complexities of their financial obligations more effectively.
More PDF Templates
Trust Amendment Template - Documenting changes creates a history of your estate planning decisions.
Understanding the eviction process is crucial for both landlords and tenants, and utilizing the correct documentation is essential for clarity and legal compliance. One important resource in this process is the Notice to Quit form, which provides a formal means for landlords to address lease violations. This form not only clarifies the expectations but also gives tenants a fair opportunity to remedy any issues before further action is taken.
Lic 603a - The form serves as a resource for ensuring that staff meet state guidelines.
Welder Performance Qualification Record - It acts as a reference point for future welding assignments and contracts.
Documents used along the form
The IRS Form 1040 is a crucial document for individual taxpayers in the United States, serving as the standard federal income tax return form. However, several other forms and documents are often used in conjunction with the 1040 to provide a complete picture of an individual's tax situation. Below is a list of six commonly associated forms and documents.
- W-2 Form: Employers provide this form to employees to report annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from their paychecks. It is essential for accurately completing the 1040.
- California 1285.65 Form: This form is essential for requesting modifications to an existing Wage and Earnings Assignment Order, particularly for adjustments due to changes in circumstances like emancipation or custody. For more details, refer to All California Forms.
- 1099 Form: This form is used to report various types of income other than wages, salaries, and tips. There are several variations of the 1099, including the 1099-MISC for freelance work and the 1099-INT for interest income.
- Schedule A: This form allows taxpayers to itemize deductions, such as medical expenses, mortgage interest, and charitable contributions, instead of taking the standard deduction.
- Schedule C: Self-employed individuals use this form to report income and expenses related to their business activities. It is essential for determining net profit or loss.
- Form 8862: Taxpayers who have previously been denied the Earned Income Tax Credit must use this form to reapply for the credit in subsequent years.
- Form 8889: This form is necessary for individuals with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). It reports contributions, distributions, and any tax implications associated with the account.
Understanding these associated forms is vital for ensuring compliance with tax regulations and maximizing potential deductions and credits. Each document plays a specific role in the overall tax filing process, contributing to a comprehensive and accurate tax return.
Form Breakdown
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The IRS 1040 form is used by individuals to file their annual income tax returns. |
| Filing Deadline | The standard deadline for filing the 1040 form is April 15th of each year. |
| Income Reporting | Taxpayers must report all sources of income, including wages, dividends, and interest. |
| Deductions | Taxpayers can choose between standard deductions and itemized deductions to reduce taxable income. |
| State-Specific Forms | Many states have their own income tax forms, governed by state tax laws, which vary by jurisdiction. |
More About IRS 1040
What is the IRS 1040 form?
The IRS 1040 form is the standard individual income tax return form used by U.S. taxpayers to report their annual income. This form allows individuals to calculate their tax liability, claim tax credits, and determine whether they owe taxes or will receive a refund. It is typically due on April 15th each year, unless that date falls on a weekend or holiday.
Who needs to file a 1040 form?
Most U.S. citizens and residents who earn income must file a 1040 form. This includes individuals who are self-employed, receive wages, or have investment income. There are certain income thresholds that determine whether you are required to file, which can vary based on your filing status, age, and type of income.
What information do I need to complete the 1040 form?
To complete the 1040 form, you will need personal information such as your name, address, and Social Security number. Additionally, you will need details about your income sources, including W-2 forms from employers, 1099 forms for freelance work, and any other relevant financial documents. You should also gather information about deductions and credits you may qualify for, such as mortgage interest or education credits.
What are the different versions of the 1040 form?
There are several versions of the 1040 form, including the 1040-SR for seniors, which features larger print and a simplified layout. Additionally, there is the 1040-NR for non-resident aliens. Each version is designed to cater to different taxpayer needs, but all serve the same primary purpose of reporting income and calculating taxes owed.
How do I file my 1040 form?
You can file your 1040 form electronically using tax preparation software or through a tax professional. Alternatively, you can complete a paper form and mail it to the appropriate IRS address. If you choose to file electronically, you may receive your refund faster than if you file by mail.
What should I do if I make a mistake on my 1040 form?
If you discover an error after submitting your 1040 form, you can file an amended return using Form 1040-X. This form allows you to correct mistakes related to income, deductions, or credits. It’s important to file an amendment as soon as you realize the error to avoid potential penalties or interest from the IRS.
IRS 1040: Usage Steps
Filling out the IRS 1040 form is an important step in filing your taxes. This form helps you report your income and determine your tax liability. Completing it accurately ensures that you fulfill your tax obligations and can help you avoid issues down the line. Below are the steps to guide you through the process of filling out the 1040 form.
- Gather all necessary documents. Collect your W-2s, 1099s, and any other income statements, as well as receipts for deductions and credits.
- Start with your personal information. Fill in your name, address, and Social Security number at the top of the form. If you are filing jointly, include your spouse's information as well.
- Report your income. Use the appropriate lines to enter your total income from various sources, such as wages, dividends, and self-employment earnings.
- Calculate your adjusted gross income (AGI). This is done by subtracting any adjustments to income, like contributions to retirement accounts, from your total income.
- Determine your deductions. Choose between the standard deduction and itemized deductions. Enter the amount on the form accordingly.
- Calculate your taxable income. Subtract your deductions from your AGI to find your taxable income.
- Determine your tax liability. Use the IRS tax tables or tax rate schedules to find out how much tax you owe based on your taxable income.
- Account for any credits. Apply any tax credits you qualify for, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit, to reduce your total tax owed.
- Complete the payment section. If you owe taxes, indicate how you plan to pay, whether by check or electronically. If you expect a refund, choose how you would like to receive it.
- Sign and date the form. If you are filing jointly, both you and your spouse must sign. Don’t forget to include your phone number and email address.
Once you have completed the form, review it for accuracy. Make sure all information is correct before submitting it to the IRS. You can file electronically or mail a paper copy, depending on your preference.